
These optimistic private-sector predictions are probably aimed at maximising investment funding. More than 30 private-sector fusion companies have recently appeared, however, promising commercial fusion reactors within 10 years. A full-scale nuclear fusion power facility will probably not be available until the 2050s.įusion research, under way since 1955, is big science, funded until recently only by governments. This improvement will be extremely difficult and expensive. The system must now be improved to the point where fusion yields a huge net energy return over the entire system end to end. Although two million joules of laser energy produced a fusion yield of three million joules, NIF invested 300 million joules to produce the lasers. NIF has proved it is possible to initiate fusion under controlled conditions, but we remain a long way from nuclear fusion-generated electricity on the public grid. The resulting fusion reaction released three million joules – a gain of 1.5 breaking the previous record of 0.7.
NIF hit the fuel pellet with two million joules of laser energy over a few billionths of a second. When gain exceeds 1.0 the fusion released more energy than the lasers put in. Nuclear fusion experiments are evaluated in terms of the ratio between the energy released in fusion and the energy imparted to the fuel by the lasers – the gain. Maintaining these conditions for long enough allows the positively charged hydrogen atoms to overcome their mutual electrical repulsion and to fuse together releasing energy. In the recent NIF breakthrough, 192 lasers zapped a 1mm pellet of deuterium/tritium fuel held inside a gold canister, compressing the pellet to 20 times the density of lead and raising the temperature to more than 5,000,000 degrees Fahrenheit, about 100 times hotter than the surface of the sun. The immense gravity of stars creates the extreme pressure conditions for fusion.ĭifferent approaches to developing practicable nuclear fusion employ different means to contain, heat and squeeze the plasma – magnetic fields at ITER, and “inertial containment” at NIF.

Intensive research is under way to develop practical fusion power, principally at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) in California and the International Experimental Thermonuclear Reactor (ITER) in France, a collaborative effort between the European Union, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States.įusion reactions take place in plasma, a super-hot, charged gas made of positive ions and freely-moving electrons, a fourth state of matter with properties distinct from solids, liquids and gases. Energy released in nuclear fission also reflects conversion of mass to energy.įusion could generate four times more energy per kilogram of fuel than fission and nearly four million times more energy than burning fossil fuel, while generating only easily-handleable waste. The speed of light is so huge that converting the tiniest amount of mass to energy releases enormous energy. This mass difference is released as energy according to Einstein’s equation E= MC2, where E is energy, M is mass and C is speed of light. Nuclear fusion means combining atoms of deuterium and tritium, two varieties of hydrogen that fuse at lower temperatures and density than ordinary hydrogen, to create new atoms with slightly less total mass.

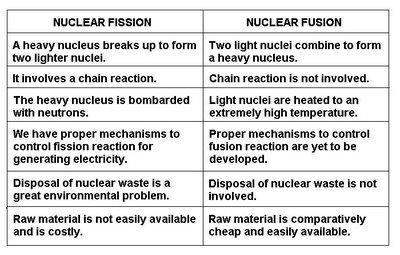
Research to develop nuclear fusion power generation recently made a major breakthrough in one area but suffered a serious setback in another. Nuclear fission is a well-established technology and could be widely deployed to supply current energy needs.īut the holy grail of energy generation is nuclear fusion, promising virtually limitless energy from plentifully available raw materials – deuterium, extractable from seawater and tritium, generated using widely-available (currently) lithium. Either of two nuclear options – nuclear fission and nuclear fusion – could generate electricity in abundance with little or no warming from carbon dioxide emissions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
